It aims to clarify the principles, advantages, and disadvantages of each method, helping businesses and accounting professionals make informed decisions. Furthermore, the article will offer practical insights into the implementation and compliance of these costing methods, ensuring that companies can align their accounting practices with GAAP standards effectively. Selling, general, and administrative costs (SG&A) are classified as period expenses. For manufacturers seeking to comprehensively understand their profitability, accurately assigning production costs to individual products is crucial.

Period Cost Misrepresentation
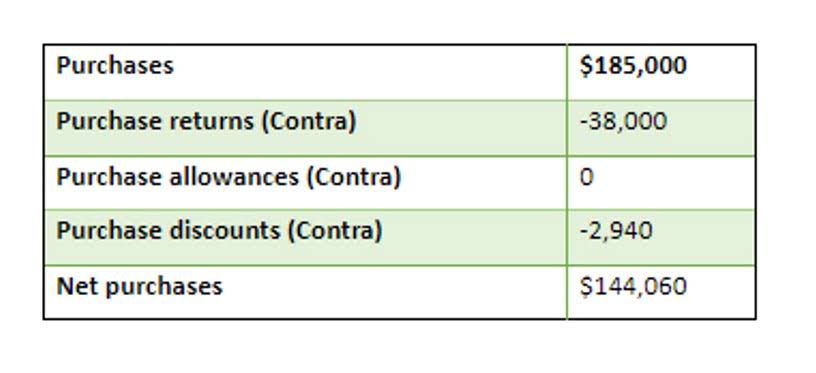
All costs are classified on functional basis as production costs, administration costs, selling costs, distribution costs. Net income on the two reports can be different if units produced do not equal units sold. Such multi-layered calculations underscore the intricate nature of absorption costing, revealing that even a seemingly simple formula can necessitate an in-depth understanding of production details and cost factors. Net income on the two reports can be differentif units produced do not equal units QuickBooks Accountant sold. Let’s look at a few examples to see how absorption costing works in the real world and how it impacts pricing decisions.
Essential for inventory valuation 🔗
Based on absorption costing methods, the additional unit appears to produce a loss of $0.50, and it appears that the correct decision is to not make the sale. Variable costing suggests a profit of $0.50, and the information appears to support a decision to make the sale. Management may well decide to sell the additional unit at $9.50 and produce an additional $0.50 for the bottom line. Remember, no other costs will be generated by accepting this proposed transaction. If management was limited to absorption costing information, this opportunity would likely have been foregone.

Absorption Costing: Meaning, Ascertainment of Profit, Advantages and Disadvantages
It is possible to use Activity-based costing (ABC) to allocate production overheads within the application of absorption costing. However, this is too time-consuming and is not very cost-effective when all we want is to allocate costs to be following GAAP/IFRS. Even if a company chooses to use variable costing for in-house accounting purposes, it still has to calculate absorption balance sheet costing to file taxes and issue other official reports. Firms that use absorption costing choose to allocate all costs to production.
- It is added back to the gross profit before reaching net profit per unit.
- This is because the higher production volume allows fixed costs to be distributed over more units, lowering the unit production cost.
- This is important for managers when making decisions about stock levels and pricing strategies.
- In the long run, all costs are to be recovered, whether it may be fixed or variable direct or indirect.
- Deskera’s inventory management software enables you to stay on top of your stock levels at all times and fulfill your customer orders with confidence.
- For instance, NetSuite Inventory offers both forward and backward traceability of inventory—a feature that is particularly advantageous for businesses with an array of products and multiple locations.
Products
- This allows the manufacturer to price its products to ensure covering all manufacturing costs.
- Even businesses with comprehensive manufacturing and managerial accounting know-how need a cohesive solution to accurately implement absorption costing principles.
- Provides an unclear picture of the profitability of the business as total fixed costs are not subtracted from the revenue.
- Absorption costing is particularly useful for businesses with high fixed overhead or complex production processes.
- This represents a significant business process improvement for many manufacturing finance teams, helping build a trustworthy base for your cost calculations.
Under variable costing, companies charge off, orexpense, all the fixed manufacturing costs during the period ratherthan deferring their expense and carrying them forward to the nextperiod as part of inventory cost. Consequently, income before income taxes under variablecosting is $600 less than under absorption costing because morecosts are expensed during the period. Overhead costs can be both fixed and variable e.g. raw material, skilled labor hour per unit, etc. However, there are indirect overheads that are fixed in nature over the period of production e.g. The absorption costing method argues for the accounting of these both fixed and variable overheads to the units produced whether or not sold by the end of the production period. The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the different costing methods under GAAP.

The variable product costs include all variable manufacturing costs (direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead). These costs are subtracted from sales to produce the variable manufacturing margin. As a result, these amounts must also be subtracted to arrive at the true contribution margin. Management must take into account all variable costs (whether related to manufacturing or SG&A) in making critical decisions. From the contribution margin are subtracted both fixed factory overhead and fixed SG&A costs. The choice between absorption costing and variable costing can also have implications for profitability analysis.

Accurate Profitability Tracking
- Specifically, a portion of the contents of the beginning inventory cup would be transferred to expense commensurate with the decrease in inventory.
- These differences are due to the treatment of fixed manufacturing costs.
- Also, the application of Absorption Costing in the production of additional units adds to the net profit of the company since there are no more fixed costs to be allocated.
- While this task may seem straightforward for companies specializing in a single or limited range of products, it becomes increasingly complex for firms with a diverse product portfolio.
- This leads to more informed decisions about pricing, production, and strategy.
- This is significant if a company ramps up production in advance of an anticipated seasonal increase in sales.
In contrast, variable costing treats fixed overhead costs as period costs and excludes them from product costs. In conclusion, absorption costing and variable costing are two distinct methods of cost allocation that differ in their treatment of fixed manufacturing overhead costs. Absorption costing includes fixed manufacturing overhead costs in the cost of each unit produced and values inventory at a higher level.
Best Suited for Small Businesses
Absorption costing is not as well understood as variable costing because of its financial statement limitations. But understanding how it can help management make decisions is very important. See the Strategic CFO forum on Absorption Cost Accounting that helps managers understand its uses to learn more. In terms of decision-making information and analysis, the absorption costing method offers little assistance. Total cost absorption for these manufacturing facilities will be uniform. Hence, these facilities will absorb full production costs and generate higher profits absorption costing formula due to economies of scale.

Leave a Reply